Joint Architecture Standard Overview Profile
Generalized Star
The generalized star topology is a topology that attempts to wire the network together in such a way that each node is the center of a small star (see Figure). Given a dimension d, these networks will have d! nodes and each node will have a fixed degree of d-1.
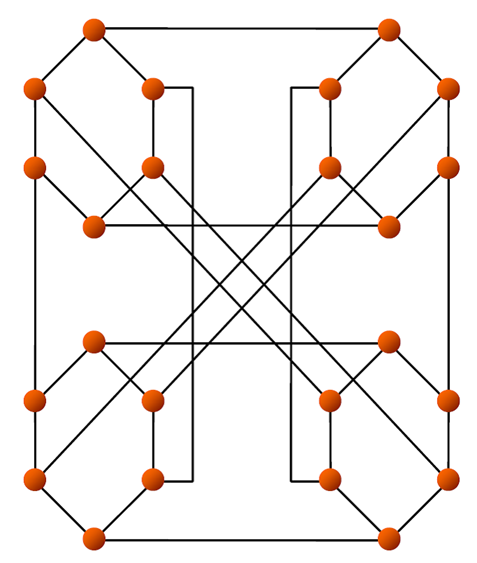
Generalized Star for d=4
This topology is good in areas of performance and complexity. Generalized stars maintain a low diameter while utilizing a low number of links. Reliability scales with the dimension of the overall network.
This topology is highly specific in structure and thus can only accommodate systems with d! (factorial) nodes (i.e., 6, 24, 120, 720, etc., nodes). The large distance between potential node counts does not make this topology feasible for our purposes.
- Advantages: Low link count, efficient use of links yielding good diameter. Reliability is good and scales with the number of nodes present.
- Disadvantages: Very specific in structure, and specific requirements on the number of nodes makes this topology a poor candidate for most systems.