Communication Profile
RapidIO Interconnect
RapidIO technology is a packetized point-to-point interconnect fabric. Packets carry user-definable payloads from 1 to 256 bytes. Both serial and parallel physical interfaces are defined, allowing effective data rates from 667 Mbps to 30 Gbps. The serial version of RapidIO was chosen for JAS because it requires a small number of connecting wires between nodes.
RapidIO systems are comprised of end point processing elements and switch processing elements. The RapidIO interconnect architecture is partitioned into a layered hierarchy of specifications which includes the Logical, Transport, and Physical Layers. Switches in RapidIO are synonymous with routers in SpaceWire.
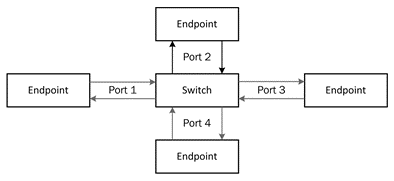
RapidIO Network
The Rapid IO specification is divided into 14 volumes. Each volume fits within one of four groups: the logical layer, the transport layer, the physical layer, and a special topics group. The breakdown is as follows:
- Logical Layer
- Part 1 – Logical I/O Specification
- Part 2 – Message Specification
- Part 5 – Global Shared Memory Specification
- Part 9 – Flow Control Specification
- Part 10 – Data Streaming Specification
- Transport Layer
- Part 3 – Transport Specification
- Part 11 – Multicast Specification
- Physical Layer
- Part 4 – Parallel Physical Specification
- Part 6 – Serial Physical Specification
- Part 12 – Virtual Output Queueing Extensions Specification
- Special Topics
- Annex I – Software/System Bring-up Specification
- Annex II – Session Management Protocol Specification
- Part 7 – System and Device Inter-operability Specification
- Part 8 – Error Management/Hot Swap Extensions Specification
RapidIO packets are formed through the combination of bit fields defined in each of the layers. The figure below shows the format of a RapidIO packet. Each layer represents a different layer of the specification. The MTU size of a RapidIO packet is 280 bytes, of which up to 256 bytes are user-definable data.
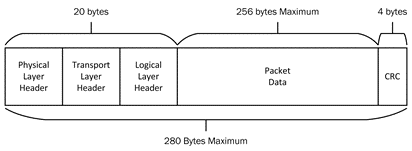
RapidIO Packet
